The Epistemic Hole: Why Commonplace XAI Fails in Authorized Reasoning
The core downside is that AI explanations and authorized justifications function on completely different epistemic planes. AI gives technical traces of decision-making, whereas regulation calls for structured, precedent-driven justification. Commonplace XAI methods consideration maps and counterfactuals fail to bridge this hole.
Consideration Maps and Authorized Hierarchies
Consideration heatmaps spotlight which textual content segments most affected a mannequin’s output. In authorized NLP, this may present weight on statutes, precedents, or details. However such surface-level focus ignores the hierarchical depth of authorized reasoning, the place the ratio decidendi issues greater than phrase prevalence. Consideration explanations danger creating an phantasm of understanding, as they present statistical correlations moderately than the layered authority construction of regulation. Since regulation derives validity from a hierarchy (statutes → precedents → rules), flat consideration weights can not meet the usual of authorized justification.
Counterfactuals and Discontinuous Authorized Guidelines
Counterfactuals ask, “what if X have been completely different?” They’re useful in exploring legal responsibility (e.g., intent as negligence vs. recklessness) however misaligned with regulation’s discontinuous guidelines: a small change can invalidate a whole framework, producing non-linear shifts. Easy counterfactuals could also be technically correct but legally meaningless. Furthermore, psychological analysis exhibits jurors’ reasoning could be biased by irrelevant, vivid counterfactuals (e.g., an “uncommon” bicyclist route), introducing distortions into authorized judgment. Thus, counterfactuals fail each technically (non-continuity) and psychologically (bias induction).
Technical Clarification vs. Authorized Justification
A key distinction exists between AI explanations (causal understanding of outputs) and authorized explanations (reasoned justification of authority). Courts require legally adequate reasoning, not mere transparency of mannequin mechanics. A “widespread regulation of XAI” will doubtless evolve, defining sufficiency case by case. Importantly, the authorized system doesn’t want AI to “assume like a lawyer,” however to “clarify itself to a lawyer” in justificatory phrases. This reframes the problem as one among information illustration and interface design: AI should translate its correlational outputs into coherent, legally legitimate chains of reasoning understandable to authorized professionals and decision-subjects.
A Path Ahead: Designing XAI for Structured Authorized Logic
To beat present XAI limits, future methods should align with authorized reasoning’s structured, hierarchical logic. A hybrid structure combining formal argumentation frameworks with LLM-based narrative era affords a path ahead.
Argumentation-Based mostly XAI
Formal argumentation frameworks shift the main focus from characteristic attribution to reasoning construction. They mannequin arguments as graphs of help/assault relations, explaining outcomes as chains of arguments prevailing over counterarguments. For instance: A1 (“Contract invalid attributable to lacking signatures”) assaults A2 (“Legitimate attributable to verbal settlement”); absent stronger help for A2, the contract is invalid. This method immediately addresses authorized rationalization wants: resolving conflicts of norms, making use of guidelines to details, and justifying interpretive selections. Frameworks like ASPIC+ formalize such reasoning, producing clear, defensible “why” explanations that mirror adversarial authorized apply—going past simplistic “what occurred.”
LLMs for Narrative Explanations
Formal frameworks guarantee construction however lack pure readability. Massive Language Fashions (LLMs) can bridge this by translating structured logic into coherent, human-centric narratives. Research present LLMs can apply doctrines just like the rule in opposition to surplusage by detecting its logic in opinions even when unnamed, demonstrating their capability for refined authorized evaluation. In a hybrid system, the argumentation core gives the verified reasoning chain, whereas the LLM serves as a “authorized scribe,” producing accessible memos or judicial-style explanations. This combines symbolic transparency with neural narrative fluency. Crucially, human oversight is required to stop LLM hallucinations (e.g., fabricated case regulation). Thus, LLMs ought to help in rationalization, not act because the supply of authorized fact.
The Regulatory Crucial: Navigating GDPR and the EU AI Act
Authorized AI is formed by GDPR and the EU AI Act, which impose complementary duties of transparency and explainability.
GDPR and the “Proper to Clarification”
Students debate whether or not GDPR creates a binding “proper to rationalization.” Nonetheless, Articles 13–15 and Recital 71 set up a de facto proper to “significant details about the logic concerned” in automated selections with authorized or equally important impact (e.g., bail, sentencing, mortgage denial). Key nuance: solely “solely automated” selections—these with out human intervention—are lined. A human’s discretionary overview removes the classification, even when superficial. This loophole permits nominal compliance whereas undermining safeguards. France’s Digital Republic Act addresses this hole by explicitly protecting decision-support methods.
EU AI Act: Danger and Systemic Transparency
The AI Act applies a risk-based framework: unacceptable, excessive, restricted, and minimal danger. Administration of justice is explicitly high-risk. Suppliers of Excessive-Danger AI Techniques (HRAIS) should meet Article 13 obligations: methods have to be designed for consumer comprehension, present clear “directions to be used,” and guarantee efficient human oversight. A public database for HRAIS provides systemic transparency, transferring past particular person rights towards public accountability.
The next desk gives a comparative evaluation of those two essential European authorized frameworks:
| Function | GDPR (Normal Knowledge Safety Regulation) | EU AI Act (EU AI Act) |
| Main Scope | Processing of non-public knowledge 25 | All AI methods, tiered by danger 22 |
| Important Focus | Particular person rights (e.g., to entry, erasure) 25 | Systemic transparency and governance 24 |
| Set off for Clarification | A choice “based mostly solely on automated processing” that has a “authorized or equally important impact” 20 | AI methods categorized as “high-risk” 22 |
| Clarification Commonplace | “Significant details about the logic concerned” 19 | “Directions to be used,” “traceability,” human oversight 24 |
| Enforcement | Knowledge Safety Authorities (DPAs) and nationwide regulation 25 | Nationwide competent authorities and the EU database for HRAIS 24 |
Legally-Knowledgeable XAI
Completely different stakeholders require tailor-made explanations:
- Choice-subjects (e.g., defendants) want legally actionable explanations for problem.
- Judges/decision-makers want legally informative justifications tied to rules and precedents.
- Builders/regulators want technical transparency to detect bias or audit compliance.
Thus, rationalization design should ask “who wants what sort of rationalization, and for what authorized goal?” moderately than assume one-size-fits-all.
The Sensible Paradox: Transparency vs. Confidentiality
Explanations have to be clear however danger exposing delicate knowledge, privilege, or proprietary data.
GenAI and Privilege Dangers
Use of public Generative AI (GenAI) in authorized apply threatens attorney-client privilege. The ABA Formal Opinion 512 stresses attorneys’ duties of technological competence, output verification, and confidentiality. Attorneys should not disclose consumer knowledge to GenAI except confidentiality is assured; knowledgeable consent could also be required for self-learning instruments. Privilege is dependent upon a cheap expectation of confidentiality. Inputting consumer knowledge into public fashions like ChatGPT dangers knowledge retention, reuse for coaching, or publicity through shareable hyperlinks, undermining confidentiality and creating discoverable “data.” Safeguarding privilege thus requires strict controls and proactive compliance methods.
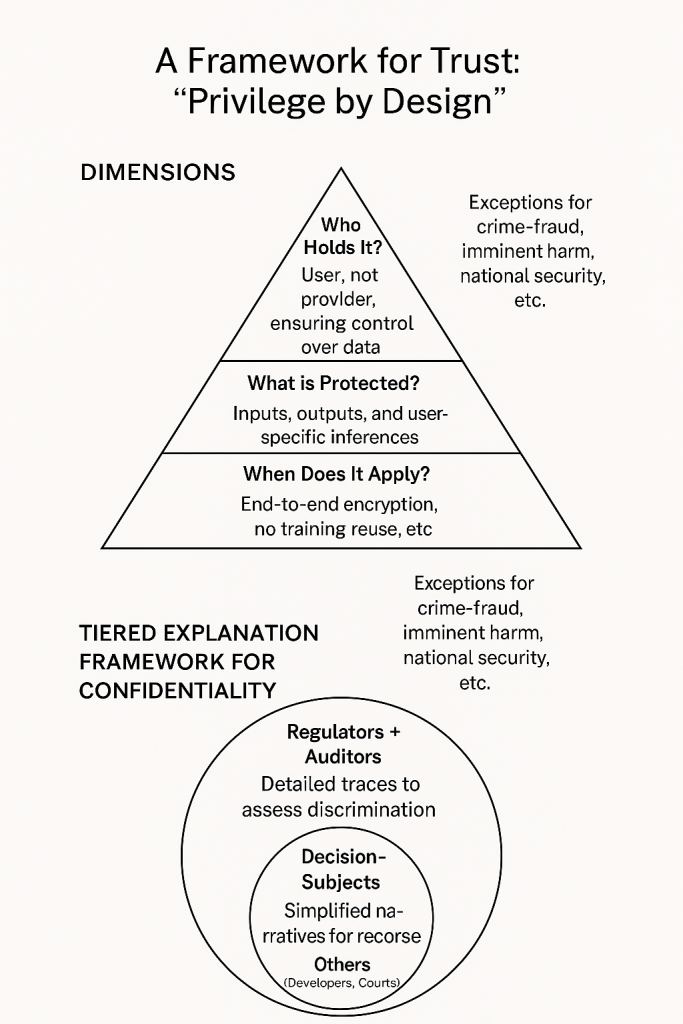
A Framework for Belief: “Privilege by Design”
To deal with dangers to confidentiality, the idea of AI privilege or “privilege by design” has been proposed as a sui generis authorized framework recognizing a brand new confidential relationship between people and clever methods. Privilege attaches provided that suppliers meet outlined technical and organizational safeguards, creating incentives for moral AI design.
Three Dimensions:
- Who holds it? The consumer, not the supplier, holds the privilege, guaranteeing management over knowledge and the power to withstand compelled disclosure.
- What’s protected? Consumer inputs, AI outputs in response, and user-specific inferences—however not the supplier’s basic information base.
- When does it apply? Solely when safeguards are in place: e.g., end-to-end encryption, prohibition of coaching reuse, safe retention, and impartial audits.
Exceptions apply for overriding public pursuits (crime-fraud, imminent hurt, nationwide safety).
Tiered Clarification Framework: To resolve the transparency–confidentiality paradox, a tiered governance mannequin gives stakeholder-specific explanations:
- Regulators/auditors: detailed, technical outputs (e.g., uncooked argumentation framework traces) to evaluate bias or discrimination.
- Choice-subjects: simplified, legally actionable narratives (e.g., LLM-generated memos) enabling contestation or recourse.
- Others (e.g., builders, courts): tailor-made ranges of entry relying on function.
Analogous to AI export controls or AI expertise classifications, this mannequin ensures “simply sufficient” disclosure for accountability whereas defending proprietary methods and delicate consumer knowledge.

References
- Consideration Mechanism for Pure Language Processing | S-Logix, accessed August 22, 2025, https://slogix.in/machine-learning/attention-mechanism-for-natural-language-processing/
- Prime 6 Most Helpful Consideration Mechanism In NLP Defined – Spot Intelligence, accessed August 22, 2025, https://spotintelligence.com/2023/01/12/attention-mechanism-in-nlp/
- The Hierarchical Mannequin and H. L. A. Hart’s Idea of Regulation – OpenEdition Journals, accessed August 22, 2025, https://journals.openedition.org/revus/2746
- Hierarchy in Worldwide Regulation: A Sketch, accessed August 22, 2025, https://academic.oup.com/ejil/article-pdf/8/4/566/6723495/8-4-566.pdf
- Counterfactual Reasoning in Litigation – Quantity Analytics, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/counterfactual-reasoning-litigation
- Counterfactual Pondering in Courtroom | Insights from Jury Analyst, accessed August 22, 2025, https://juryanalyst.com/counterfactual-thinking-courtroom/
- (PDF) Explainable AI and Regulation: An Evidential Survey – ResearchGate, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/376661358_Explainable_AI_and_Law_An_Evidential_Survey
- Can XAI strategies fulfill authorized obligations of transparency, reason- giving and authorized justification? – CISPA, accessed August 22, 2025, https://cispa.de/elsa/2024/ELSA%20%20D3.4%20Short%20Report.pdf
- THE JUDICIAL DEMAND FOR EXPLAINABLE ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, accessed August 22, 2025, https://columbialawreview.org/content/the-judicial-demand-for-explainable-artificial-intelligence/
- Authorized Frameworks for XAI Applied sciences, accessed August 22, 2025, https://xaiworldconference.com/2025/legal-frameworks-for-xai-technologies/
- Argumentation for Explainable AI – DICE Analysis Group, accessed August 22, 2025, https://dice-research.org/teaching/ArgXAI2025/
- Argumentation and rationalization within the regulation – PMC – PubMed Central, accessed August 22, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10507624/
- Argumentation and rationalization within the regulation – Frontiers, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/artificial-intelligence/articles/10.3389/frai.2023.1130559/full
- College of Groningen A proper framework for combining authorized …, accessed August 22, 2025, https://research.rug.nl/files/697552965/everything23.pdf
- LLMs for Explainable AI: A Complete Survey – arXiv, accessed August 22, 2025, https://arxiv.org/html/2504.00125v1
- How one can Use Massive Language Fashions for Empirical Authorized Analysis, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.law.upenn.edu/live/files/12812-3choillmsforempiricallegalresearchpdf
- Positive-Tuning Massive Language Fashions for Authorized Reasoning: Strategies & Challenges – Regulation.co, accessed August 22, 2025, https://law.co/blog/fine-tuning-large-language-models-for-legal-reasoning
- How Massive Language Fashions (LLMs) Can Rework Authorized Business – Springs – Customized AI Compliance Options For Enterprises, accessed August 22, 2025, https://springsapps.com/knowledge/how-large-language-models-llms-can-transform-legal-industry
- Significant data and the proper to rationalization | Worldwide Knowledge Privateness Regulation, accessed August 22, 2025, https://academic.oup.com/idpl/article/7/4/233/4762325
- Proper to rationalization – Wikipedia, accessed August 22, 2025, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Right_to_explanation
- What does the UK GDPR say about automated decision-making and …, accessed August 22, 2025, https://ico.org.uk/for-organisations/uk-gdpr-guidance-and-resources/individual-rights/automated-decision-making-and-profiling/what-does-the-uk-gdpr-say-about-automated-decision-making-and-profiling/
- The EU AI Act: What Companies Want To Know | Insights – Skadden, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.skadden.com/insights/publications/2024/06/quarterly-insights/the-eu-ai-act-what-businesses-need-to-know
- AI Act | Shaping Europe’s digital future – European Union, accessed August 22, 2025, https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/regulatory-framework-ai
- Key Subject 5: Transparency Obligations – EU AI Act, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.euaiact.com/key-issue/5
- Your rights in relation to automated resolution making, together with profiling (Article 22 of the GDPR) | Knowledge Safety Fee, accessed August 22, 2025, http://dataprotection.ie/en/individuals/know-your-rights/your-rights-relation-automated-decision-making-including-profiling
- Legally-Knowledgeable Explainable AI – arXiv, accessed August 22, 2025, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.10708
- Holistic Explainable AI (H-XAI): Extending Transparency Past Builders in AI-Pushed Choice Making – arXiv, accessed August 22, 2025, https://arxiv.org/html/2508.05792v1
- When AI Conversations Turn out to be Compliance Dangers: Rethinking …, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/when-ai-conversations-become-compliance-9205824/
- Privilege Issues When Utilizing Generative Synthetic Intelligence in Authorized Apply, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.frantzward.com/privilege-considerations-when-using-generative-artificial-intelligence-in-legal-practice/
- ABA Formal Opinion 512: The Paradigm for Generative AI in Authorized Apply – UNC Regulation Library – The College of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, accessed August 22, 2025, https://library.law.unc.edu/2025/02/aba-formal-opinion-512-the-paradigm-for-generative-ai-in-legal-practice/
- Ethics for Attorneys on GenAI Use: ABA Formal Opinion #512 | Jenkins Regulation Library, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.jenkinslaw.org/blog/2024/08/08/ethics-attorneys-genai-use-aba-formal-opinion-512
- AI in Authorized: Balancing Innovation with Accountability, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.legalpracticeintelligence.com/blogs/practice-intelligence/ai-in-legal-balancing-innovation-with-accountability
- AI privilege: Defending consumer interactions with generative AI – ITLawCo, accessed August 22, 2025, https://itlawco.com/ai-privilege-protecting-user-interactions-with-generative-ai/
- The privacy-explainability trade-off: unraveling the impacts of differential privateness and federated studying on attribution strategies – Frontiers, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/artificial-intelligence/articles/10.3389/frai.2024.1236947/full
- Differential Privateness – Belfer Middle, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.belfercenter.org/sites/default/files/2024-08/diffprivacy-3.pdf
- Understanding the Synthetic Intelligence Diffusion Framework: Can Export Controls Create a … – RAND, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.rand.org/pubs/perspectives/PEA3776-1.html
- Technical Tiers: A New Classification Framework for International AI Workforce Evaluation, accessed August 22, 2025, https://www.interface-eu.org/publications/technical-tiers-in-ai-talent
Aabis Islam is a pupil pursuing a BA LLB at Nationwide Regulation College, Delhi. With a robust curiosity in AI Regulation, Aabis is captivated with exploring the intersection of synthetic intelligence and authorized frameworks. Devoted to understanding the implications of AI in varied authorized contexts, Aabis is eager on investigating the developments in AI applied sciences and their sensible functions within the authorized area.
